| Original author(s) | Jean-Pierre Charras |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | KiCad developers[1] |
| Initial release | 1992; 29 years ago[2] |
| Stable release | 5.1.10 / 3 May 2021; 13 days ago |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++[3] |
| Operating system | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| Available in | 23 languages[4] |
| Type | EDA |
| License | GNU GPL v3+[5] |
| Website | www.kicad.org |
The following library files are available: Symbols - Schematic symbol libraries; Footprints - PCB footprint libraries; 3D models - 3D model data; Cloning Libraries. Users who wish to keep up to date with the latest libraries should clone the KiCad libraries using Git or SVN. Cloning the library repositories means that users only need to. KiCad is a full feature electronics development application for the design and manufacture of electronics that runs natively on Windows, OSX, and Linux. Application suite includes: schematic capture, printed circuit board layout, Gerber file viewer, solid model viewer, and much more. Icloud Photo Library Free Up Space On Mac Xsan Mac File Library Kicad Library Location Mac How To Add Sparkfun Library To Eagle On Mac Where Is Library On A Mac How To Get Rid Disk Space On Mac Library Cache Duplicate Photos Library Mac Library Mail Mac Delete Mac Library Doesn't Have Frameworks How To Add A Script To Indd Script Library Mac. KiCad for Mac is a suite of open source electronic PCB design software that allows users to create electronic charts and printed circuits. KiCad for Mac includes a wide range of features and parameters that will help you in PCB design.The software has a complex but easy-to-use interface that allows you to quickly and easily design your charts. At the same time, KiCad for Mac gives. Click on the Add existing library to table button: E. Navigate to the directory where you cloned the Digi-Key KiCad Library. Navigate to the digikey-symbols folder within digikey-kicad-library folder. At this point you can add one library at a time or all of the libraries.
KiCad (pronounced 'Key-CAD'[6]) is a free software suite for electronic design automation (EDA). It facilitates the design of schematics for electronic circuits and their conversion to PCB designs. KiCad was originally developed by Jean-Pierre Charras. It features an integrated environment for schematic capture and PCB layout design. Tools exist within the package to create a bill of materials, artwork, Gerber files, and 3D views of the PCB and its components.
History[edit]

KiCad was created in 1992 by Jean-Pierre Charras while working at IUT de Grenoble.[7] Since then KiCad has gained a number of both volunteer and paid contributors. Notably in 2013 the CERN BE-CO-HT section started contributing resources towards KiCad to help foster open hardware development by helping improve KiCad to be on par with commercial EDA tools.
KiCad adopted a point release versioning scheme in December 2015 starting with KiCad 4.0.0. This was the first release featuring the more advanced tools implemented by CERN developers. CERN hopes to contribute further to the development of KiCad by hiring a developer through donations. Contributions may be made through the links on KiCad's website.
Components[edit]

The KiCad suite has five main parts:
KiCad– the project manager.Eeschema– the schematic capture editor.Pcbnew– the PCB layout program. It also has a 3D view.GerbView– the Gerber viewer.Bitmap2Component– tool to convert images to footprints for PCB artwork.
Features[edit]
Kicad Library Location Macon Ga
KiCad uses an integrated environment for all of the stages of the design process: Schematic capture, PCB layout, Gerber file generation/visualization, and library editing.

KiCad is a cross-platform program, written in C++ with wxWidgets to run on FreeBSD, Linux, Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. Many component libraries are available, and users can add custom components. The custom components can be available on a per-project basis or installed for use in any project. There are also tools to help with importing components from other EDA applications, for instance EAGLE. There are also third party libraries available for KiCad, including SnapEDA, and the Digi-Key KiCad Library.[8] Configuration files are in well documented plain text, which helps with interfacing version control systems, as well as with automated component generation scripts.
Localisation[edit]
Multiple languages are supported, such as Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese, Czech, Dutch, English, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Lithuanian, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Slovak, Slovene, Spanish, and Swedish.
Eeschema[edit]
Kicad Library Location Macon
Eeschema has features including hierarchical schematic sheets, custom symbol creation, and an ERC (electrical rules check). Schematic symbols in Eeschema are very loosely coupled to footprints in Pcbnew to encourage reuse of footprints and symbols (e.g. a single 0805 footprint can be used for capacitors, resistors, inductors, etc.).
Pcbnew[edit]
Internally Pcbnew supports up to 32 copper layers and 32 technical layers. Dimensions are stored with nanometer precision in signed 32-bit integers making the theoretical maximal PCB dimension 231 nm, or approximately 2.14 meters.
Currently[citation needed] Pcbnew is being heavily refactored, including getting a new rendering engine (called the graphics abstraction layer, or GAL) with OpenGL and Cairo back ends. Pcbnew is also getting a new tool framework to more easily allow developers to add tools without having to deal with supporting multiple renderers. Due to this some tools are only available on the legacy XOR-based renderer and some are only available with the GAL renderers.
KiCad had a built-in autorouter for basic, single connections (since removed from the suite). Alternatively, Alfons Wirtz's open-source Java-based FreeRouting[9] can be used to externally autoroute boards. Anthony Blake's Toporouter, a topological autorouter developed in 2008 for gEDAPCB as a Google-funded open source project mentored by DJ Delorie,[10] has been adapted for use with KiCad as well.
A DRC (design rules check) is available to check for common logical errors.
The 3D PCB viewing function is based on VRML models, and the board model can be exported for CAD integration.
Some recent[citation needed] additions follow.
An interactive router, which features the ability to walk around existing traces in the way or shove existing traces into a different position while maintaining their connectivity.
High-speed PCB routing tools such as track-length matching and differential pair support.
Python scripting support.
Community[edit]
On 12 March 2015 Olimex Ltd,[11] a provider of development tools and embedded device programmers, announced that they have switched from EAGLE to KiCad as their primary EDA tool.[12]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^''KiCad Developers' team'. Archived from the original on 2018-07-29. Retrieved 2018-07-29.
- ^Halvick, Remy (2007-07-08). 'Re: About KiCad first release'. kicad-users.
[…] JP Charras said me that the first drafts were made in 1992 for a DOS version, but not diffused […]
- ^Manveru (2009-10-13). 'KiCad'. Archived from the original on 2018-07-29. Retrieved 2011-01-20.
- ^'kicad-i18n - Translations for KiCad source code'.
- ^'KiCad Program License'. Archived from the original on 2018-07-29. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- ^Stambaugh, Wayne (2018-02-03) [2018]. 'KiCad Version 5 New Feature Demo'. Archived from the original on 2018-07-29.
- ^'Kicad'. iut-tice.ujf-grenoble.fr. Archived from the original on 2015-12-21. Retrieved 2015-12-29.
- ^'Digi-Key KiCad Library'.
- ^Wirtz, Alfons (2014-03-08) [2004]. 'FreeRouting - Printed Circuit Board Routing Software from FreeRouting.net'. Archived from the original on 2017-09-23. Retrieved 2017-09-24.
- ^Blake, Anthony (2009-07-07) [2008]. 'Topological Autorouter - Introduction'. Archived from the original on 2011-02-27.
- ^'Olimex Ltd.'
- ^'Our first two small KiCAD OSHW boards are ready!'. 2015-03-12. Archived from the original on 2015-03-17.
External links[edit]
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Kicad |
Kicad Library Location Mac
Kicad Library Location Machine
There are several different ways to manage third party libraries like this one. Using git clone is a great way to keep it up to date.
How you decide to manage the library(s) within KiCad is open to debate, but the way I prefer to use them is to pull them in to the Project Libraries, that way they are managed separately from the default libraries, this can be done as such:
git clone https://github.com/Digi-Key/digikey-kicad-library.gitinto your preferred directoryOpen KiCad
Import the symbols:
A. Open Symbol Editor or Schematic editor
B. Click on Preferences then on Manage Symbol Libraries…
C. Click on the Project Specific Libraries tab:
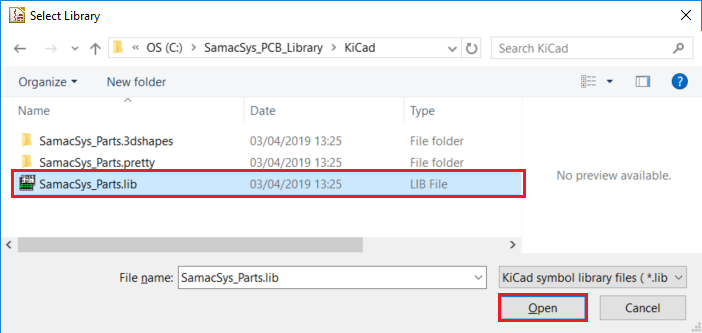
D. Click on the Add existing library to table button:
E. Navigate to the directory where you cloned the Digi-Key KiCad Library
F. Navigate to the digikey-symbols folder within digikey-kicad-library folder
G. At this point you can add one library at a time or all of the libraries. To add all of the libraries click on any one of the the libraries and then press
Ctrl+a. This will select all of the libraries, then click the Open button.H. You should now see the libraries in the table:
Import the footprints(similar process to symbols):
A. Open Footprint editor or PCB Layout
B. Click on Preferences then on Manage Footprint Libraries…
C. Click on the Project Specific Libraries tab:
D. Click on the Add existing library to table button:
E. Navigate to the directory where you cloned the Digi-Key KiCad Library
F. Expand the digikey-kicad-library folder and select digikey-footprints.pretty
G. Click OK
H. The digikey-footprints should now show in your library table